Home » Posts tagged 'Soybean'
Tag Archives: Soybean
Double Crop Options After Wheat (KSU Edition)
Stolen from the KSU e-Update June 5th 2025.
Double cropping after wheat harvest can be a high-risk venture for grain crops. The remaining growing season is relatively short. Hot and/or dry conditions in July and August may cause problems with germination, emergence, seed set, or grain fill. Ample soil moisture this year can aid in establishing a successful crop after wheat harvest. Double-cropping forages after wheat works well even in drier regions of the state.
The most common double crop grain options are soybean, sorghum, and sunflower. Other possibilities include summer annual forages and specialized crops such as proso millet or other short-season summer crops, even corn. Cover crops are also an option for planting after wheat (see the companion eUpdate article “Cover crops grown post-wheat for forage”).
Be aware of herbicide carryover potential
One major planting consideration after wheat is the potential for herbicide carryover. Many herbicides applied to wheat are Group 2 herbicides in the sulfonylurea family with the potential to remain in the soil after harvest. If a herbicide such as chlorsulfuron (Glean, Finesse, others) or metsulfuron (Ally) has been used, then the most tolerant double crop will be sulfonylurea-resistant varieties of soybean (STS, SR, Bolt) or other crops. When choosing to use herbicide-resistant varieties, be sure to match the resistance trait with the specific herbicide (not only the herbicide group) that you used. This is especially true when looking at sunflowers as a double crop. There are sunflowers with the Clearfield trait, which allows Beyond herbicide applications, and ExpressSun sunflowers, which allow an application of Express herbicide. While both of these herbicides are Group 2 (ALS-inhibiting herbicides), the Clearfield trait and ExpressSun are not interchangeable, and plant damage can result from other Group 2 herbicides.
Less information is available regarding the herbicide carryover potential of wheat herbicides to cover crops. There is little or no mention of rotational restrictions for specific cover crops on the labels of most herbicides. However, this does not mean there are no restrictions. Generally, there will be a statement that indicates “no other crops” should be planted for a specified amount of time, or that a bioassay must be conducted prior to planting the crop.
Burndown of summer annual weeds present at planting is essential for successful double-cropping. Assuming glyphosate-resistant kochia and pigweeds are present, combinations of glyphosate with products such as saflufenacil (Sharpen) or tiafenacil (Reviton), or alternative treatments such as paraquat may be required. Dicamba or 2,4-D may also be considered if the soybean varieties with appropriate herbicide resistance traits are planted. In addition, residual herbicides for the double crop should be applied at this time.
Management, production costs, and yield outlooks for double crop options are discussed below.
Soybeans
Soybeans are likely the most commonly used crop for double cropping, especially in central and eastern Kansas (Figure 1). With glyphosate-resistant varieties, often the only production cost for planting double crop soybeans was the seed, an application of glyphosate, and the fuel and equipment costs associated with planting, spraying, and harvesting. However, the spread of herbicide-resistant weeds means additional herbicides will be required to achieve acceptable control and minimize the risk of further development of resistant weeds.

Weed control. The weed control cost cannot really be counted against the soybeans, since that cost should occur whether or not a soybean crop is present. In fact, having soybeans on the field may reduce herbicide costs compared to leaving the field fallow. Still, it is recommended to apply a pre-emergence residual herbicide before or at planting time. Later in the summer, a healthy soybean canopy may suppress weeds enough that a late-summer post-emergence application may not be needed.
Variety selection for double cropping is important. Soybeans flower in response to a combination of temperature and day length, so shifting to an earlier-maturing variety when planting late in a double crop situation will result in very short plants with pods that are close to the ground. Planting a variety with the same or perhaps even slightly later maturity rating (compared to soybeans planted at a typical planting date) will allow the plant to develop a larger canopy before flowering. Planting a variety that is too much later in maturity, however, increases the risk that the beans may not mature before frost, especially if long periods of drought slow growth. The goal is to maximize the length of the growing season of the crop, so prompt planting after wheat harvest time is critical. The earlier you can plant, the higher the yield potential of the crop if moisture is not a limiting factor.
Fertilizer considerations. Adding some nitrogen (N) to double-crop soybeans may be beneficial if the previous wheat yield was high and the soil N was depleted. A soil test before wheat harvest for N levels is recommended. Use no more than 30 lbs/acre of N. It would be ideal to knife-in the fertilizer. If that is not possible, banding it on the soil surface would be acceptable. Do not apply N in the furrow with soybean seed as severe stand loss can occur.
Seeding rates and row spacing. Seeding rate can be slightly increased if soybeans are planted too late in order to increase canopy development. Narrow row spacing (15-inch or less) has often resulted in a yield advantage compared to 30-inch rows in late plantings. Soybeans planted in narrow rows will canopy over more quickly than in wide rows, which is important when the length of the growing season is shortened. Narrow rows also offer the benefits of increasing early-season light capture, suppressing weeds, and reducing erosion. On the other hand, the advantage of planting in wide rows is that the bottom pods will usually be slightly higher off the soil surface to aid harvest. The other consideration is planting equipment. Often, no-till planters will handle wheat residue better and place seeds more precisely than drills, although the difference has narrowed in recent years.
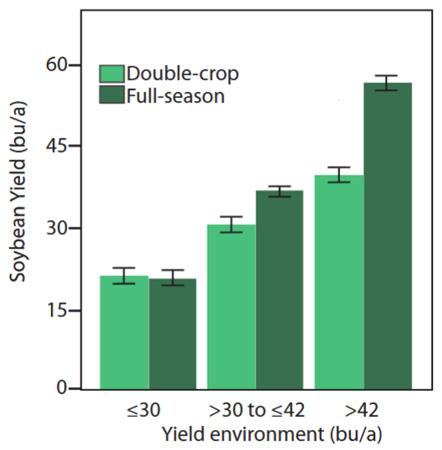
What are typical yield expectations for double-crop soybeans? It varies considerably depending on moisture and temperature, but yields are usually several bushels less than full-season soybeans. A long-term average of 20 bushels per acre is often mentioned when discussing double-crop soybeans in central and northeast Kansas. Rainfall amount and distribution can cause a wide variation in yields from year to year. Double-crop soybean yields typically are much better as you move farther southeast in Kansas, often ranging from 20 to 40 bushels per acre.
A recent publication explores the potential yield of double-crop soybeans relative to full-season yield (Figure 2) and the most limiting factors affecting the yields for double-crop soybeans. The link to this article is: https://bookstore.ksre.ksu.edu/pubs/MF3461.pdf.
Grain Sorghum
Grain sorghum is another double crop option. Unlike soybeans, sorghum hybrids for double cropping should be earlier maturing hybrids. Sorghum development is primarily driven by the accumulation of heat units, and the double crop growing season is too short to allow medium-late or late hybrids to mature before the first frost in most of Kansas.
Seeding rates and row spacing. Late-planted sorghum likely will not tiller as much as early plantings and can benefit from slightly higher seeding rates than would be used for sorghum planted at an earlier date. Narrow row spacing is advised, especially if the outlook for rainfall is good.
Fertilizer considerations. A key component for the estimation of N application rates is the yield potential. This will largely determine the N needs. It is also important to consider potential residual N from the wheat crop. This can be particularly important when wheat yields are lower than expected. In that situation, additional available N may be present in the soil. Assess the amount of profile N by taking soil samples at a depth of 24 inches and submitting them for analysis at a soil testing laboratory.
Double crop sorghum planted into average or greater-than-average amounts of wheat residue can result in a challenging amount of residue to deal with when planting next year’s crop. Nitrogen fertilizer can be tied up by wheat residue, so use application methods to minimize tie-up, such as knifing into the soil below the residue.
Weed control. Weed control can be important in double-crop sorghum. Warm-season annual grasses, such as crabgrass, can reduce double-crop sorghum yields. Using a chloroacetamide-and-atrazine pre-emergence product may be key to successful double-crop sorghum production. Herbicide-resistant grain sorghum varieties will allow the use of imazamox (Imiflex in igrowth sorghums) or quizalofop (FirstAct in DoubleTeam grain sorghum) that can control summer annual grasses.
No-till studies at Hesston documented 4-year average double crop sorghum yields of 75 bushels per acre compared to about 90 bushels per acre for full-season sorghum. A different 10-year study that did not have double crop planting but did compare early- and late-planting dates averaged 73 bushels per acre for May planting vs. 68 bushels per acre for June planting.
Sunflowers
Sunflowers can be a successful double crop option anywhere in the state, provided there is enough moisture at planting time to get a stand. Sunflowers need more moisture than any other crop to germinate and emerge because of the large seed. Therefore, stand establishment is important. Planting immediately after wheat harvest on a limited irrigation field can be a good fit to help with stand establishment.
Seeding rates and hybrid selection. When double-cropping sunflowers, producers should use similar seeding rates to what is typical for the area for full-season sunflowers. While full-season sunflowers can be successful in double-crop production, utilizing shorter-season hybrids can increase the likelihood of the sunflowers blooming and maturing before a killing frost.
Weed control. First, it is important to check the herbicide applications on the wheat. The rotation restriction to sunflowers after several commonly used wheat herbicides is 22-24 months.
Weed control can be an issue with double-crop sunflowers since herbicide options are limited, especially post-emergence. Thus, controlling weeds prior to sunflower planting is critical and may be complicated pre-plant restrictions for some herbicides. Planting Clearfield or ExpressSun sunflowers will provide additional post-emergence herbicide options, but ALS-resistant kochia and pigweeds still won’t be controlled. Imazamox (Beyond in Clearfield sunflower) has activity on small annual grasses as well as many broadleaf weeds, if they are not ALS-resistant.
Summer annual forages
With mid-July plantings, and where herbicide carryover issues are not a concern, summer annual sorghum-type forages are also a good double crop option. A study planted July 21, 2008 near Holton, when summer rainfall was very favorable, provided yields of 2.5 to 3 tons dry matter/acre for hybrid pearl millet and sudangrass at the low end to 4 to 5 tons dry matter/acre for forage sorghum, BMR forage sorghum, photoperiod sensitive forage sorghum, and sorghum x sudangrass hybrids. Earlier plantings may produce even more tonnage, as long as there is adequate August rainfall.
One challenge with late-planted summer annual forages is getting them to dry down when harvest is delayed until mid- to late-September. Wrapping bales or bagging to make silage are good ways to deal with the higher moisture forage this late in the year.
Corn
Is double-crop corn a viable option? Corn is typically not recommended for late June or July plantings because yield is usually substantially less than when planted earlier.
Typically, mid-July planted corn struggles during pollination and seldom receives sufficient heat units to fill grain before frost. Very short-season corn hybrids (80 to 95 RM) have the greatest chance of maturing before frost in double crop plantings, but generally have less yield potential when compared to hybrids of 100 RM or more used for full-season plantings. Short-season hybrids often set the ear fairly close to the ground, increasing the harvest difficulty. Glyphosate-resistant hybrids will make weed control easier with double crop corn, but problems remain present with late-emerging summer weeds such as pigweeds, velvetleaf, and large crabgrass. Keep in mind, corn is very susceptible to carryover of most residual ALS herbicides used in wheat.
Considerations for altering seeding rates and variety/hybrid maturity for the crops discussed above are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1. Seeding rate and variety/hybrid relative maturity considerations for double crops compared to full-season.
| Crop | Seeding rate | Relative maturity |
| ???????? Difference between double crop and full-season ???????? | ||
| Soybean | Increase | No change or longer |
| Sorghum | Increase | Shorter |
| Sunflower | No change | Shorter |
| Corn | No change | Shorter |
Volunteer wheat control
One of the issues with double cropping that is often overlooked by producers is the potential for volunteer wheat in the crop following wheat. If volunteer wheat emerges and goes uncontrolled, it can cause serious problems for nearby wheat fields in the fall as a host for the wheat streak mosaic complex of viruses [wheat streak mosaic (WSMV), High Plains disease (HPD), and triticum mosaic (TriMV)] that are transmitted by the wheat curl mite (WCM).
Volunteer wheat can generally be controlled fairly well with glyphosate or Group 1 herbicides such as quizalofop (Assure II, others), clethodim (Select Max, others), or sethodydim (Poast Plus, others), but control is reduced during times of drought stress. Atrazine can provide control of volunteer wheat in double-crop corn or sorghum, but control can be erratic depending on rainfall patterns.
For more detailed information about herbicides, see the “2025 Chemical Weed Control for Field Crops, Pastures, and Noncropland” guide available online at https://www.bookstore.ksre.ksu.edu/pubs/CHEMWEEDGUIDE.pdf or check with your local K-State Research and Extension office for a paper copy. The use of trade names is for clarity to readers and does not imply endorsement of a particular product, nor does exclusion imply non-approval. Always consult the herbicide label for the most current use requirements.
To Subscribe to the KSU Agronomy E-Updates follow this link
https://eupdate.agronomy.ksu.edu/index_new_prep.php
Authors contributing to the post
Sarah Lancaster, Weed Management Specialist
slancaster@ksu.edu
John Holman, Cropping Systems Agronomist
jholman@ksu.edu
Logan Simon, Southwest Area Agronomist
lsimon@ksu.edu
Tina Sullivan, Northeast Area Agronomist
tsullivan@ksu.edu
Jeanne Falk Jones, Multi-County Agronomist
jfalkjones@ksu.edu
PRE-EMERGENT RESIDUAL HERBICIDE ACTIVITY ON SOYBEANS, 2025
Liberty Galvin, Weed Science Specialist
Karina Beneton, Weed Science Graduate Student.
Objective
Determine the duration of residual weed control in soybean systems following the application of Preemergent (PRE) herbicides when applied alone and in tank-mix combination.
Why we are doing the research
PRE herbicides offer an effective means of suppressing early-season weed emergence, thereby minimizing competition during the critical early growth stage. However, evolving herbicide resistance and the need for longer-lasting weed suppression underscore the importance of evaluating multiple modes of action and their residual properties alone and tank-mixed.
Field application experimental design and methods
Field experiments were conducted in 2022, 2023, and 2024 growing seasons in Bixby, Lane, and Ft. Cobb FRSU Research Stations across Oklahoma. Each herbicide (listed in Table 1) was tested individually, in 2-way combinations, 3-way mixtures, and finally as 4-way combinations that included all active ingredients listed at the label rate.
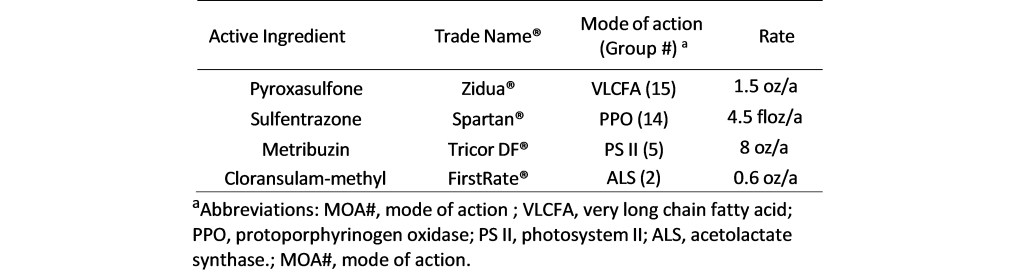
Soybeans were planted at rates between 116,000 and 139,000 seeds/acre from late May to early June, depending on the year and location. The variety used belongs to the indeterminate mid- maturity group IV, with traits conferring tolerance to glyphosate (group 9 mode of action), glufosinate (group 10), and dicamba (group 4). Not all soybean varieties have metribuzin tolerance. Please read the herbicide label and consult your seed dealer for acquiring tolerant varieties. Row spacing was 76 cm at Bixby and Lane, and 91 cm at Fort Cobb. PRE treatments were applied immediately after planting at each experimental location.
POST applications consisted of a tank-mix of dicamba (XtendiMax VG® – 22 floz/acre), glyphosate (Roundup PowerMax 3®- 30 floz/acre), S-metolachlor (Dual II Magnum® – 16 floz/acre), and potassium carbonate (Sentris® – 18 floz/acre). Applications were made on different dates, mostly after the first 3 weeks following PRE treatments. These timings were based on visual weed control ratings, particularly for herbicides applied alone or in 2-way combinations, which showed less than 80% control at those early evaluation dates. The need for POST applications also depended on the species present at each site, with most fields being dominated by pigweed, as illustrated in the figure below.
Results
Tank-mixed PRE herbicide combinations generally provided superior residual control compared to a single mode of action application (Shown in Figure 1). Timely post-emergent (POST) herbicide applications helped sustain high levels of weed suppression, particularly as the effectiveness of residual PRE declined.
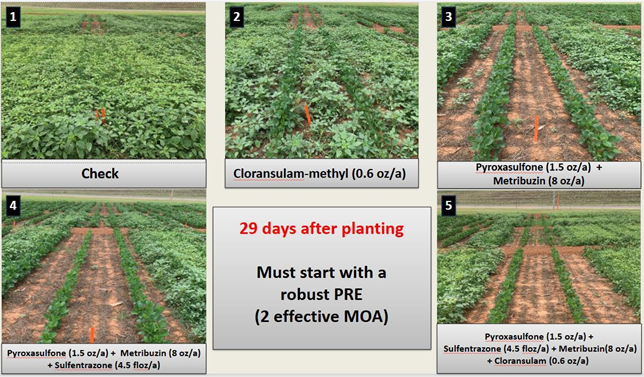
Residual control of tank-mixed PRE
Some herbicides applied alone or in simple 2-way mixes, such as sulfentrazone + chloransulam- methyl and pyroxasulfone + chloransulam-methyl required POST applications within 20 to 29 days after PRE, indicating moderate residual control.
In contrast, 2-way combinations containing metribuzin, such as sulfentrazone + metribuzin and pyroxasulfone + metribuzin, extended control up to 50 days after PRE in some cases, highlighting metribuzin’s importance even in less complex formulations.
Furthermore, 3-way and 4-way combinations including metribuzin provided the longest-lasting control, delaying POST applications up to 51–55 days after PRE.
Injury of specific weeds
Palmer amaranth (Amaranthus palmeri) control in Bixby was consistently high (≥90%) at 2 weeks after PRE in 2022 and 2024 across all treatments. At 4 WAPRE, treatments containing metribuzin alone or in combination maintained strong control (90% or greater).
Texas millet (i.e., panicum; Urochloa texana) and large crabgrass (Digitaria sanguinalis) were effectively managed with most treatments delivering over 90% control early in the season and maintaining performance throughout. In 2024, control remained generally effective, though pyroxasulfone alone showed a temporary lack of control for Texas millet, and single applications declined in effectiveness against large crabgrass later in the season. These reductions were likely due to continuous emergence and the natural decline in residual herbicide activity due to weather. The most consistent late-season control for both species came from 3- and 4-way herbicide combinations.
Morningglory (Ipomoea purpurea) control reached full effectiveness (100%) only when POST herbicides were applied, across all years and locations. Their late emergence beyond the residual window of PRE herbicides reinforces the importance of sequential herbicide applications for season-long control.
Take home messages:
- Incorporating PRE and POST herbicides slows the rate of herbicide resistance
- Tank mixing with *different modes of action* ensures greater weed control by having activity on multiple metabolic pathways within the plant.
- Tank mixing with PRE herbicides could reduce the number of POST applications required, and
- Provides POST application flexibility due to residual of PRE application
For additional information, please contact Liberty Galvin at 405-334-7676 | LBGALVIN@OKSTATE.EDU or your Area Agronomist extension specialist.
Management of soybean inoculum
Josh Lofton, Cropping Systems Specialist
Brian Arnall, Precision Nutrient Management Specialist
Soybean, a legume, can form a symbiotic relationship with Bradyrhizobium japonicum (Kirchner, Buchanan) and create their N to supplement crop demands. However, this relationship depends upon these beneficial microorganisms’ presence and persistence in the soil. This specific strain of microorganisms is not native to Oklahoma and thus must be supplemented using inoculum as a seed treatment. However, the use of inoculums alone does not guarantee a successful relationship. Handling, storage, soil conditions, and other factors can impact the ability of these microorganisms to do their job.
Soybean nitrogen demand is high, with most reports indicating that soybeans need 4.5 to 5.0 pounds of nitrogen per bushel of grain yield. This means that a 30-bushel crop requires between 135 and 150 pounds of nitrogen per acre (in comparison, corn and wheat need only 0.8 or1.6 pounds, respectively). This relationship has been shown to supply an equivalent of 89 lbs of N to the soil. In the previous example, these bacteria could fulfill 50-90% of nitrogen demand, reducing input costs significantly.
However, the bacteria associated with soybean inoculum are living organisms. Therefore, the conditions they experience before being applied to the seed and after treatment (including both before and following planting) can significantly impact their relationship with the soybean plant and, thus, their ability to provide N to the plant. By introducing a high concentration of bacteria near the seed and emerging root, this symbiotic relationship is more likely to be established quickly.
The importance of using inoculum is often debated in Oklahoma, particularly given the fluctuating prices of commodities and inputs. A recent assessment of various soybean-producing areas throughout the state revealed that most fields experienced advantages from incorporating soybean inoculation (Figure 1).

These benefits can be seen when the inoculum maintains viability until it is planted. It is always recommended that the bacteria be stored in a cool, dark environment before application on the seed. These conditions help preserve the survival of these bacteria outside of the host relationship. An evaluation of soybean inoculant after being stored short-term in different conditions found that in as little as 14 days, viability can decrease when kept in non-climate-controlled conditions (Figure 2). Additionally, viability was further reduced at 21 days when stored at room temperature compared to a refrigerated system

However, conditions colder than this, such as the use of a freezer, can compromise survival as well. Storing inoculum in the freezer forms ice crystals within the living cells and damages the cell membranes, making the microorganisms less likely to be alive upon rethawing. Additional chemicals can be added to increase the viability of long-term storage and sub-freezing temperatures. From an application standpoint, a new product should be purchased if additional storage is needed beyond short-term storage.
An additional question frequently arises: “How often should I inoculate my soybean?” As mentioned, these bacteria are not native to Oklahoma. As a result, they are not well adapted to survive in our environment and must outcompete native populations in the soil. Additionally, periods of hot and dry conditions appear to reduce the bacteria’s ability to survive without a host, the soybean roots. These are conditions we often observe in Oklahoma systems. Therefore, inoculation should be applied with every soybean planting to ensure a sufficient population of these bacteria. These bacteria promote root nodulation and nitrogen fixation in the soil.
Other soil conditions, such as excessively dry or wet soils, high or low pH, and residual nutrients, can also impact the persistence of these microorganisms. Of these, soil pH has the biggest impact on the survival of these bacteria. High pH is less of a concern to Oklahoma production systems; however, soil with lower pH should be remediated. Like many bacterial systems, these bacteria optimally function at a pH range that closely resembles the ideal pH range for most crops. Lowering the soil pH below a critical threshold reduces the viability of the bacteria, hampers N-fixation processes, and diminishes the capacity of both the bacteria and soybean plants to form and maintain this relationship. While applying inoculum to soybean seeds in these adverse soil conditions can provide some advantages (Figure 3), but it often doesn’t increase yields. Therefore, inoculation with corresponding adjustments to soil pH represents the best approach.


While using inoculum is not a new concept, it is important to highlight the benefits it can provide when utilized correctly. The potential to reduce N input costs is attractive, but the effectiveness depends on proper handling, storage, and soil conditions until it can intercept the host. To maximize benefits, inoculum should be stored in a cool, dark environment and utilized in a timely manner. If there is doubt that there are not enough bacteria, an inoculum should be added. Oklahoma’s climate, particularly hot and dry conditions, can limit bacteria survival, reinforcing the need to treat the inoculum until it is in the ground carefully. Additionally, considering the soil environment is important to sustain the population of bacteria until it can inoculate its host. Emphasis on these small details can have a large impact on the plant’s ability to fix nitrogen and optimize productivity throughout the growing season.
TAKE HOMES
* Soybean requires more lbs of N per bushel than most grain crops.
* Soybeans symbiotic relationship with rhizobia can provide the majority of this nitrogen.
* Soybean rhizobia is not native to Oklahoma soils so should be added to first year soybean fields.
* Inoculum should be treated with care to insure proper nodulation.
* Due to Oklahoma’s climate and existing soil conditions rhizobia may not persist from year to year.
Any questions or comments feel free to contact Dr. Lofton or myself
josh.lofton@okstate.edu
b.arnall@okstate.edu
Appreciation of the Oklahoma Soybean Board for their support of this project.
Top-dress Wheat with P and K ??
Brian Arnall, Precision Nutrient Management Extension Specialist
Hunter Lovewell, Past PNM MS student.
Original Blog Name: Managing P and K in a wheat Double-crop Soybean System.
I planned to wait until the soybean yields came in to share the data from this project, but the wheat results are just too interesting this year.
So the trial posed the question, when is the best time to apply the phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) for the soybean crop in a wheat double crop soybean system, if any is needed above what is applied for the wheat crop. We applied the wheat’s P&K at establishment, but the soybeans P&K was applied either at wheat establishment, top-dress wheat timing, or post wheat harvest pre soybean planting. We used the sources of granular triple super phosphate (0-46-0) and potash (0-0-60) for all applications. We hypothesized the wheat crop would not benefit from the soybeans portion of P&K and that the top-dress application timing for the soybeans P&K would result in the greatest soybean yields.

So far, we have six site years with completed cycles with locations at the Eastern Research Station (ERS) near Haskell, Oklahoma, Ballagh Family Research Farm (BF) near Newkirk, Oklahoma, Skagg Family Farm (SF) near Lamont, Oklahoma, and Lake Carl Blackwell Research Farm (LCB) near Perry, Oklahoma. The research was conducted during the 2019-2020 growing season and the 2020-2021 growing season. For the 2021-2022 cycle we added two more locations one again on the Skagg Family farm and the second on a new cooperator, O’Neil Farms (OF) near Ponca City. For all locations no P or K was applied by the farmers at any point, but they did manage IPM. See location descriptions below.

The first two years of work is written up in Mr. Hunter Lovewell’s thesis titled “EFFECTS OF PHOSPHOROUS AND POTASSIUM APPLICATION TIMING ON A WHEAT DOUBLE-CROP SOYBEAN SYSTEM” which I can share with those interested. To be honest, Hunter had a couple tough seasons. Basically where wheat did well, beans typically failed and where you had good beans the previous wheat had failed. All the same he had some interesting results. What follows is pulled from his conclusions.
“While a significant response to the application of P and K was limited, the results show that there are environments in which the wheat crop can benefit from additional P and K fertilizer applied for the soybean crop. In the case of the soil (SF-SH) with low M3P and an acidic soil pH, the additional P applied during the winter wheat growing season, intended for soybeans, alleviated the aluminum toxicity issues with acidic pH, increasing wheat yields. Beyond the single location with low soil test P and pH no other significant response was found to the addition of and P. This may be explained in that most locations were only marginally deficient P and the majority of the varieties used in the study were considered to have acid soil tolerance. Penn and Arnall (2015) found that cultivars with aluminum tolerance had increased P use efficiency. The BF location showed a significant wheat grain yield response to the K fertilization, but the additional K applied for the soybean crop showed no benefit for the wheat crop. While there was no significant increase in soybean grain yield to the additional K fertilizer observations suggest that the application of K fertilizer for soybeans may be of benefit. As was mentioned before the double-crop system is susceptible to yield-limiting conditions, heat, and moisture, due to the maturity of the crop during the peak summer months. The soybean grain yields achieved in this study were all below the previous five-year yield average for all the locations. The low achieved yields and crop stress may have limited this study’s ability to identify a significant response to the application of fertilizer. “
So, one of the most interesting finding from the first six sites was that topdressing P increased yield of the wheat crop on the soil that had low pH and P. And since the P recs applied were only considering STP values and not soil pH, we had underapplied P for the wheat.
Now moving on to the 2021-22 season. Well as most of the famers know, this season has been a doozy. That said, we were not able to establish the treatments until February 1st. Therefor in the case of the 2021-22 wheat season the first application of P&K was made at top-dress timing and then the second application was made post wheat harvest. So, we are unable to say how a preplant wheat P&K application would have performed. But the wheat grain yield response to P&K was better than I could have ever imagined.
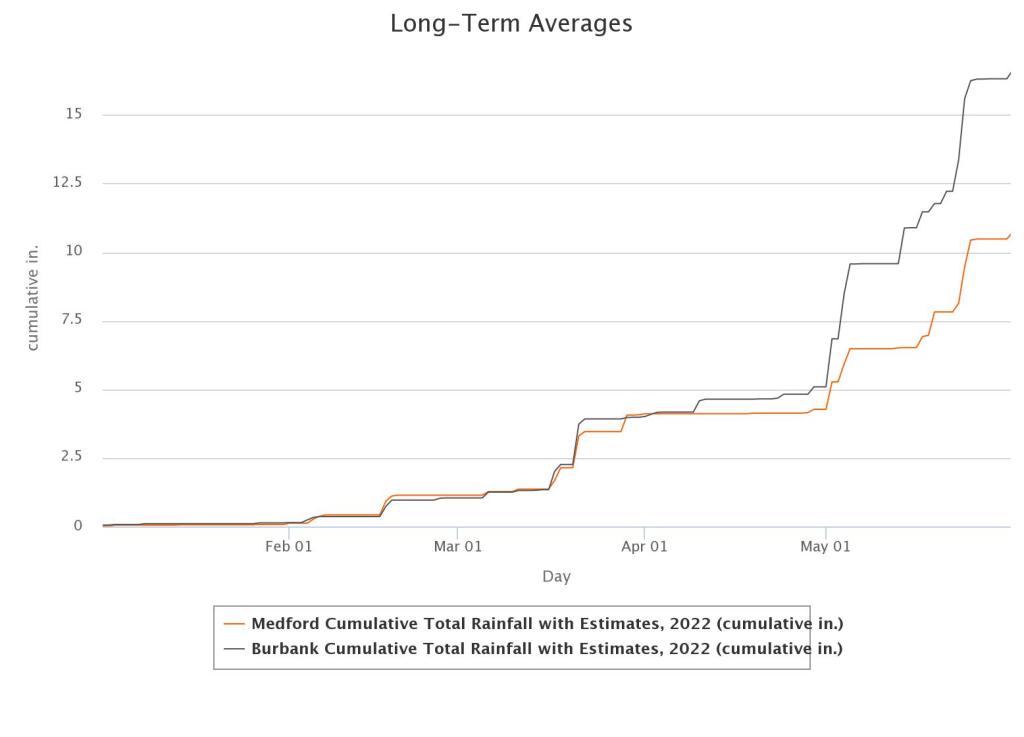
The rain post application (Feb 1st) was marginal but better than other areas in the central/southern Plains. There was about 1” of precipitation in February, almost 3” in March and under 0.2” in April. May rains for the OF site near Burbank aided in allowing the yields to climb, maxed out at 82 bushels per acre, while the SF-Nfld missed out on many of the late rains and yields topped out at 39 bushels.
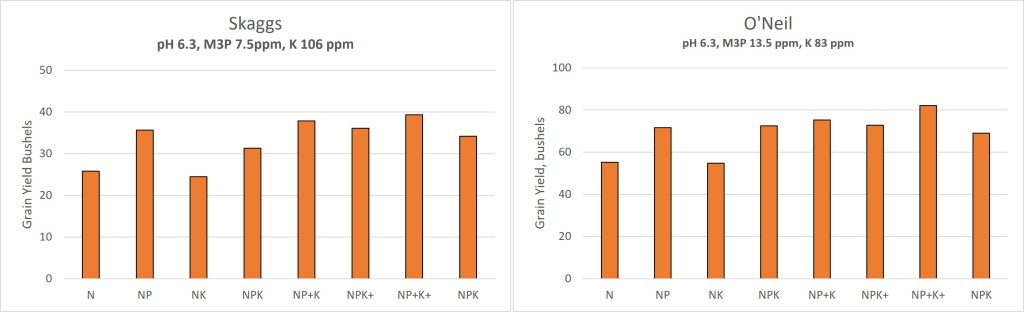
At both sites there is a clear and distinct response to P fertilizer. Note the N and NK treatments significantly lower than all other treatments. The last column on each figure title NPK is the average of all other treatments that only received the wheats P&K rate and had yet had the soybeans P&K applications.
We were able to statistically analyze the locations together by calculating a relative yield for each location. This is done by dividing the yield of each plot by the yield of the N only treatment, we did this for each replication. We then ran a t-test to look at significant treatment difference, so below any treatments that has the letters above the columns, such as an ab and b, are not statistically different at a 95% level.

The relative yield data was able to confirm that across both locations an application of P in February significantly increased yields at a consistent level of 30-50%. It is interesting that while the NP+K+ treatment almost sorts out as being statistically the highest.
While I am not even close to suggesting that you should delay application of P fertilizer in wheat production, I am a big fan of in-furrow applications, this work does point to opportunities. Such as the ability to return to the field after the wheat is up and apply broadcast P if perhaps you could not at planting. But specifically, the potential for in-season Variable Rate phosphorus based upon crop response, maybe a P-Rich strip. What I can tell you this means is that I have more work to do. First, I need a better understand of when and where this is possible. Then it is time to figure out how to use this to our advantage to more efficiently use P fertilizer.
I do want to reiterate, I am not suggesting to move away from Preplant P nor in-furrow.
Keep an eye out for the soybean data because hopefully we catch a few good rains and find out if the timing of P&K will impact the double crop yields.
I want to send a big Thank you to all the cooperators who have put up with me and my time over years to get this data and the Oklahoma Soybean Board for their continued support of this project.
Feel free to send any questions for comments my way at b.arnall@okstate.edu
Double Crop Response to Additional N, P, K and S.
Vaughn Reed, PhD. Student Precision Nutrient Management
Brain Arnall Precision Nutrient Management Extension Specialist.
Data presented below are the results of Mr. Reeds Masters research project.
On farm research trials are important, because they give us the ability to see responses over a larger geographic area, and even more importantly, evaluate our recommendations on fields that are managed by producers, not researchers. They also allow us to look at current production practices and see if there are any missed opportunities. Several years ago, we looked at whether producers were leaving yield on the table by not applying enough nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium(K), and sulfur (S) to winter wheat. We did this by applying strips of N, P, K, and S fertilizer on farmers’ fields with the instructions to not change their fertilizer management strategies. If one or more of the strips resulted in higher yields then it could be assumed that either the nutrient was under-applied by the producer, or in the case of N, lost. That study concluded that at 75% of the locations, yield was maximized by the producer with [their respective] NPKS management system, however the greatest responses came from the addition of P and that Oklahoma State University’s soil testing and analysis was adequate for nutrient recommendations. That studies results were published in 2017 and is open access, so available for anyone to read. https://dl.sciencesocieties.org/publications/cftm/abstracts/3/1/cftm2017.02.0014
There are many producers around the state that follow winter wheat with double crops (DC). Often, this practice is done with limited inputs to reduce economic risk. Oklahoma State does not make different recommendations for DC or full season crops, with the exception that yield potentials can differ. In 2016 and 2017 we duplicated the Wheat NPKS study across 3 double crops (soybean, grain sorghum, sunflower) following winter wheat and canola. With a recent climb in DC yields we wanted to investigate if producers were applying enough nutrients to maximize grain yield. Additionally it would allow us evaluate the accuracy of OSU’s soil test based fertilizer recommendations in a double crop. Over the two years, 61 on-farm sites ranging from central to NE Oklahoma had 200 lb/ac of product per nutrient applied in strips 6ft wide by 150 ft long. Urea (46-0-0), triple super phosphate (0-46-0), muriate of potash (0-0-60), and gypsum (0-0-0-19) were used for sources N, P, K, and S, respectively (92 lbs N, 92 lbs P, 120 lbs K, 38 lbs S). In most cases the fertilizer was applied post planting and post-emergence to ensure strips were applied an areas with good stand.
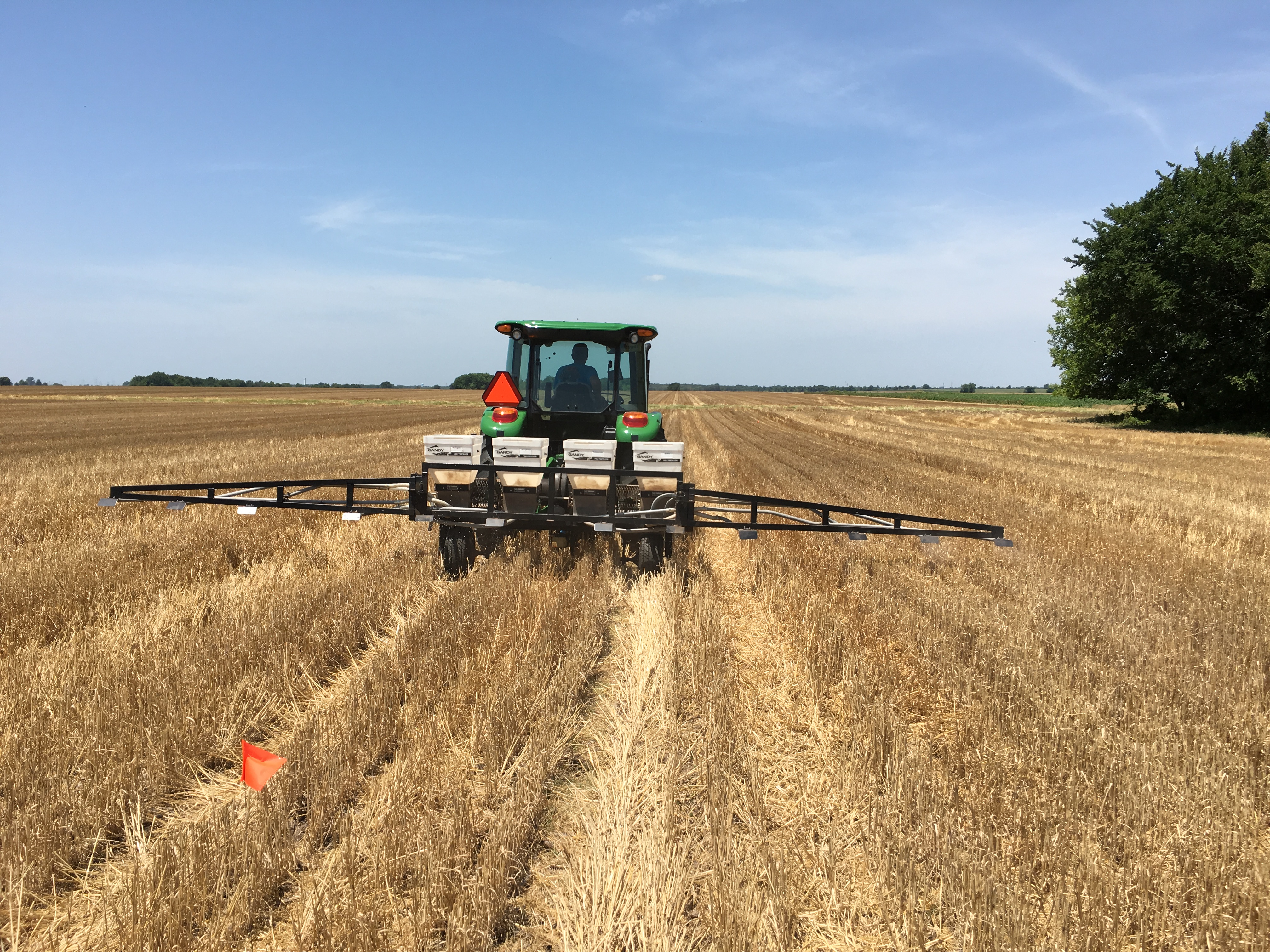

NPKS Strip Applicator. This ground driven 3pt rig uses Gandy boxes to deliver fertilizer into tubes which is then blown, by a PTO driven fan, out into strips 6 feet wide, per box. This applicator was putting out 200 lbs of Urea, 0-46-0, potash, and gypsum out per acre.
Much like with the wheat-NPKS study 75% of the locations did not respond to additional fertilizer. Twenty treatment comparisons of the 244 made across all 61 locations (50 soybean, 7 grain sorghum, 4 sunflower) yielded a statistically significant change in yield due to the addition of N-P-K-or S. For this report, a comparison was the yield of each nutrient versus the non-treated check, therefore there were four comparisons made per location. Seventeen of the twenty positive responses were found in soybean, three with grain sorghum, and no responses were found in sunflower plots. Lack of response from grain sorghum and sunflower locations is contributed to small amount of grain sorghum and sunflower fields in the study.
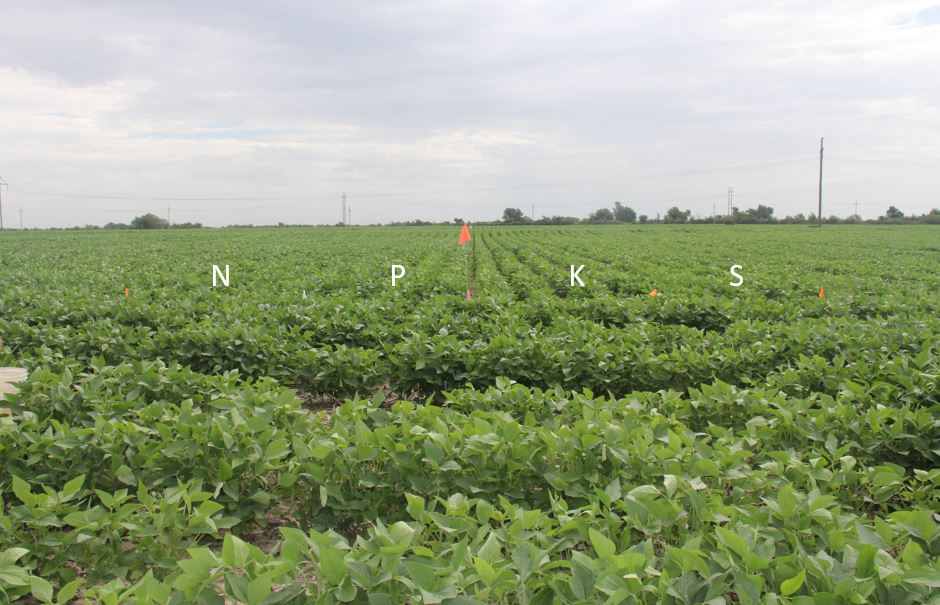

Double crop soybeans in Ottawa County with strips of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and sulfur applied post plant.
Nitrogen rates, for non-legumous crops, are yield driven, meaning the higher yielding a crop, the higher amount of N required. Both grain sorghum and sunflower crops, due to neither being legumes, were expected to see N response, especially to those locations that applied little to no N to begin with. A yield response from the addition of N was found in one grain sorghum location, where the producer application was not enough to maximize yield, and the additional N pushed the yields. As expected, there were no soybean locations that responded to the addition of N.
Phosphorus and potassium are both sufficiency based, not yield driven. This means that if the soil is at 100% sufficiency, the crop will produce at its highest rate achievable, based on that nutrient. 100% sufficiency for P and K are approximately 65 STP and 250 STK, respectively. Phosphorus and potassium strips yielded the most results, especially in soybean locations. Of 20 responses, five responses were due to P, ten due to K, and four due to S. Locations that responded to the addition to P were locations that either had low levels of STP (approx. 80% sufficiency or less), or had low pH, which leads to less availability of P (pH>5.0).
Potassium yielded the most positive results, with ten responsive locations, as well as the most interesting results, with only three sites falling below 100% sufficiency. The other responses were attributed to having low Cl levels (Cl, as in Chloride, which while responses are rare, is a necessary nutrient, and sometimes can lead to losses in yield, especially in sandy environments), as well as drought stress conditions. Potassium has been shown to have a vital role in nutrient uptake and water retention, as it is found to be critical for root growth, and these are displayed highest in crops found in drought like conditions. One hypothesis for the K response is related to root growth. The later planted DC will spend less resources in root development before going reproductive. Soybean is a heavy user of K, combine smaller roots, typically hot drier soils, and high K demand it is not surprising to find this occurrence.
Sulfur, while not wide-spread reported in Oklahoma, has recommendations by OSU built on a yield driven scale. There were four responsive locations found in this project. While one location had low soil test S values there were located areas that received high rainfall events during the growing season, and therefore the response was attributed to leaching of S.
So, after all that, what is the bottom line? Here is our observations:
- Producers maximized yield 75% of the time, with 25% of locations responding to any additional nutrient.
- The 20 responses to additional nutrients occurred across 15 locations, four locations had responses to more than one nutrient
- By nutrient: Note for P and K, due to site variability it was not expected to observe statistic yield increase due to P or K unless soil test was below 70% sufficiency, of which no location had soil test P or K below 70%.
- 38 locations were below 100% sufficiency of phosphorus, with five observed responses
- Seven locations were below 100% sufficiency of potassium, two observed responses. An additional eight locations responded that were not predicted by soil test
- Based on pre-plant soil test there were no sites expected to respond to the addition of Sulfur, 4 locations did respond.
- Soil test results were adequate in correctly identifying locations that would not respond to the addition of nutrients (93.5% accurate), while not as accurate at predicting sites that would respond.
- For K, soil testing was less accurate, as eight of the ten responsive locations had soil test values above 250 soil test K (125 ppm or 100% sufficiency). For this reason, we are currently doing work evaluating K recommendations for soybeans.
This work confirms that of the fields we evaluated, the majority was not yield limited by N, P, K or S. However, as with anything, we have more work to do in order to further refine our recommendations, and always looking to learn more about how to aid producers.
Results from 1st year of Soybean Starter Work
In the spring of 2014 we initiated what was to be the first year of a three year project evaluating starter fertilizers for soybean production in the southern Great Plains. The first and second year was and is being funded by the Oklahoma Soybean Board.
Year one was a bit experimental in that with so many products on the market we needed some initial work to help focus the direction for years two and three. I also added a treatment which I knew would have significant negative impact, for extension reasons. Keep in mind two locations in a single year does not make an experiment nor provide enough information to draw a definite conclusion. It is however enough to learn some lessons from and for us to plan for our 2015 trials.
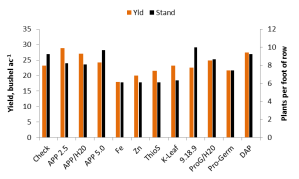
The 2014 trial consisted of 12 treatments, Figure 1 and Figure 2. In these treatments I wanted to see the impact of a standard practice, see if a specific nutrient may be more so beneficial, and evaluate a few popular products. The spring of 2014 started out dry so at one of our two locations we pre-watered. This was done by hauling water to the Lake Carl Blackwell (LCB) 1000 gallons at a time and pumping through sprinklers. The other site, Perkins, we delayed planting until we had moisture.

Image taken while planting the Soybean Starter study at Perkins. A CO2 system was used to deliver starter fertilizers with seed.
The two locations were also selected due to differences in soil fertility. The LCB site is has good soil fertility, with exception of phosphorus (P), and the Perkins site pH was an issue. I would have expected a benefit from adding P at both of these locations. Figure 4 shows the soil test results.
At LCB as expected some of the treatments (Thio-Sul) reduced stand, some unexpectedly reduced stand (Fe) and others had less impact on stand (APP 5.0) than expected. The growth at LCB was tremendous, the 30 in rows covered over very quickly and the majority of the treatments hit me waist high by early August (I am 6’0”). Many of the treatments showed greater growth than check. But when it comes down to it, grain pays and green does not. Statistically there were no treatments that out preformed the un-treated check, however the K-Leaf and 9-18-9 did make 3 and 2 bpa more than the check respectively. What I am hypothesizing at this site is that the added nutrients, especially those with high P levels, significantly increased vegetative grown and these big plants were delayed into going reproductive and they started setting pods later in much hotter weather. While riding in the combine I could see that the plots with compact plants with clearly defined rows out yielded those were the vines had crossed over and we harvested through more of a solid mat of mature plants. A hot August is not uncommon and I am curious on whether this trend repeats itself. If it does this may direct us into research evaluating ways to force/promote the reproductive stage to start in these big plants. Even if we can force flowering to start earlier, it’s unknown whether yields will increase or not.

The Check plot at LCB were plants noticeably a bit smaller and more yellow than the neighbors with phosphorus.
The same trends in treatments reducing stand can be seen at Perkins, however the impact was less extreme. Perkins being planted later due to waiting on moisture forced a later flowering date and I believe reduced overall yields. But the addition of P at this low pH site definitely made a difference. While again no treatments were statistically greater than the un-treated check the 2.5 gpa APP, DAP broadcast, APP/H2O, and Pro-Germ/H20 treatments increased yield by 5.6, 4.2, 3.8 and 1.7 bpa respectively.
Take home from year one was that at LCB the addition of a starter fertilizer had little benefit and if done wrong could cost you yield while at the low pH site of Perkins an addition 2.5 gallons of APP did get a 5 bpa bump, but do to variability in the trial the increase was not statistically significant. This year we will drop some of the treatments and incorporate a few new treatments. Based on the current weather we look to potentially being able to start with better soil moisture at planting. Again do not take this work and significantly adjust any plans you have for your 2015 soybean crop. This is however some interesting findings that I wanted to share and make everyone aware of. Finally thank you to the Oklahoma Soybean Board for providing funding for this work. www.oksoy.org/
Agriculture Apps, 200 strong and growing
It was just 11 months ago when I wrote my last blog on Ag apps. Since that time I have presented on the topic several times, added nearly 100 new apps, have filmed several designated segment on sunup featuring apps (these can be seen at http://www.youtube.com/osunpk), and released two (soon to be three) apps myself. Below is the introductory slide I have been using in all of my app talks, on this slide you can see how the number of apps have been increasing overtime. In this update I wanted to share some of the new sections I have added to manage the vast number apps and go through some of my favorite apps in each of the sections.
Finding the right app has not changed as I still just give an app 3 minutes before a keep or drop decision is made, however since a year ago some of the key words are now less useful. For example a search for wheat will bring up droves of gluten free diet apps. None of these fit the bill for what I am looking for. Though out the blog you can click on pictures screenshots to get a better view of the app buttons.
Ag News and Weather
Still a very large section with little change for my recommendations, just go with what suits you in layout and reporting. I personally use RonOnRON (Ron Hays, the voice of Oklahoma Agriculture), DTN/PF, AG/Web, and AgWired.
Ag Resources
This includes peer review publications, resource guides and extension materials.
Calculators
The majority of the Calculator apps preform relatively simple functions without the need of cellular or wifi connectivity. The Ag PhDs have two apps in the section I want to highlight, HarvestLoss and Fert. Removal. Both apps are useful tools in making management decisions. HarvestLoss allows the user to calculate the economic loss of a poorly set combine while Fert. Removal allows the user to select from a wide range of crops and see an exit ate of nutrient removal based upon selected yield level. Other useful apps are Growing Degree which allows the user to see cumulative heat units a crop has received anywhere in the US, Corn Yield Calc estimates corn yield based on ear girth and length, Canola Calc is a great apps produced by Pioneer which calculates the proper planting rate of canola based upon several factors and the Kansas Wheat Yield Calculator KWYC, uses growth stage stalk counts, height and/or NDVI to estimate potential grain yield.
Crop Tools
This section is filled with University Extension handbooks such as Purdue’s Field Guide ($12.99), University of Arkansas Corn Advisor, University of Kentucky Corn Production, and one private groups MFA Agronomy. Each of these guides are quality apps and should be chosen based upon geography or personal preference. The university apps mirror their respective hard copies however UK’s app added a nice update section highlighting local Ag news. MFA’s app is strong in pesticides with good herbicide performance data.
Fertilizer
For any producer who regularly applies animal waste the Manure Calc by the University of Nebraska is a great tool. The University of Wisconsin has a nice app in N Price Calculator and the Saskatchewan Soil Conservation association (SSCA) has created a nice fertilizer blend app. Oklahoma State University has Ammonia Loss Calculator which uses soil pH and environmental conditions to estimate N losses from surface applied urea.
OSUNPK
I am also getting into the app game with two recently released apps the Canola Starter and Field Guide. Canola Starter provides a recommendation for safe starter rates based on row width and fertilizer source. Field Guide is app version of my Nutrient Management Field Guide, this app includes a nutrient removal calculator, nutrient deficiency ID tool, and fertilizer rate calculators. Along with these I have several in the wings with titles like Crop Nutrients in Irrigation, GDDs>0, and Wildlife FoodPlot.
ID Tools
As mentioned in my first two blogs the University of Missouri’s IDWeeds app was the first taxonomy based weed identification tool. I still use it regularly but both BASF and Monsanto have brought products to the table, both named WeedID, that are very user friendly and effective. Plant Images ($5.00) is a library of nutrient deficiency photos from a large selection of crops. Years and Ag PhDs also have apps available with deficiency images named Yara Checkit and Crop Nutrient Deficiencies. Cereal Disease ID app by BASF is intended for the UK and DuPonts Pestbook for Australian cotton farmers but I find that both can be very useful even in Oklahoma.
Pay to Play, Registrations
I have heard several good things about many of these apps. However they reguire the user to either be an employee or patron of the company or online registration. In a pay to pay app I would expect an all inclusive tool that could replace several free apps and preform record keeping duties.
Records
To be honest this is not a section I use much as I do not have an operation to maintain records on. However just by walking through the apps Crop Calculator by the University of Wisconsin and Pesticide Recordkeeping (PeRK) by University of Nebraska.
Scouting/Mapping
This section has apps that I classify as decision aid tools that could be used by someone scouting crops and apps that can be used to map and or collect field notes. South Dakota State has two great tools in Soy Diseases and NPIPM Soybean Guide. Scout and Sirrus.
Seed Select
Company based, Pioneers app products are some of the best with Plantability and Estimator
Sprayer Chemical
Some things haven’t changed I still use Tank Mix Calc and Spray Select on a very regular basis. But over the past year a few companies have added product finders and Clemson University has released a very nice sprayer calibration app named Calibrate.
Weather
The last two apps are Mesonet and Climate Corp Basic. You will notice the background on the screen shot is slightly different. That is because neither of these apps is kept Ina folder, both are on my home screen. Whether it is rain, temp, or wind weather impacts all aspects of agriculture therefore these two apps are always within one tap. For any producer in Oklahoma the Mesonet is an amazing system with 120 automated weather stations spread evenly across the state. This app just provides this data with just a few swipes of the finger. For those outside of Ok Climate Basic allows producers to first save field of interest and then monitor rainfall and environmental conditions of each field. While not extremely accurate it is defiantly close enough for those with a wide territory to be a very handy app.
For more information and some screen shots of the apps in action either visit my website http://npk.okstate.edu/presentations or my YouTube site http://www.youtube.com/osunpk under the playlist OSU_NPK on Sunup.
Ag Apps Updated
Since my Ag App post in July I have presented on the topic an additional five times and have two more on the books for 2014. A good thing about doing talks is that you have to update the information to remain current. Which in all honesty, when it comes to technology of any kind this is quite challenging and even more so for Smart Phone Apps. In July when I first blogged on the subject I had 76 apps on my iPad. Today (1.3.14) I have 111 apps on my iPad, for both the iPhone and iPad, that I deem to be Ag related. Since the summer I have found new favorites, changed some, and added categories but for the most part I still maintain my 2 minute rule stated in the first blog. I have allowed a bit more leniency in that I now say “If I cannot figure it out in 3 minutes it’s GONE. An app should be intuitive, easy to use and have a purpose. They only exception to the 3 minute rule is the Scouting and Mapping Apps. Because of their complexity I allow them 5 minutes, and then I am done. Any app with GIS in its name gets much more time” I guess I am just getting soft.
Again I must make the obligatory statement; I am not a developer, designer, or expert. I am just a user who has had a chance to look at a few apps. Almost all of the apps I have are free and I am sure I have missed a few. Please share those with me. I am also not discussing Mobi’s, this is another large group of quality decision aid tools. I am also not discussing none apples apps. This is not because they are not relevant or important, it is because I do not have that technology.
I now have nine Ag folders on my iPad:
Ag News/Weather/Markets, Scouting/Mapping, Record Keeping, ID Tools, Crop Tools, Calculators, Sprayer/Chemicals, Fertilizer, Seed Select.
Apps are nice because the majority are stand alone and do not need internet or cell connection. This means they can be used when you are in the middle of nowhere, which is a great deal of Oklahoma, and have no service. This will exclude many of the Ag News/Weather/Markets, Scouting/Mapping, and Record Keeping apps that need positioning or location information.
Now let’s discuss some of the new and old apps.
Ag News/Weather/Markets
Not much change in this group however I have added one or two.
Scouting/Mapping
This category has changed the most. Record keeping apps have been removed and several new apps added. The only free apps which can create boundaries are still Scout and Sirrus. To date Scout remains to be my favorite app for in field scouting notes. Pictures tagged with Lat Long and a note is very useful. My knock on is app is its boundary creation. It is a challenge every time as it is hard to remember the steps and not make a mistake. That is where Sirrus comes to play, by far the best boundary creation app. Sirrus has easy to use tools for both point and pivot boundaries. I like the edit vertex zoom in tool that resembles a rifle scope. I was able to add 12 fields in a matter of 20 minutes. Being able to create grid soil sampling scheme and record samples is also a very nice tool. My favorite part of the app, the UNDO button, and all apps should include this. The drawback to Sirrus is that it has no ability to take notes such as Scout. An additional nice scouting tool is South Dakota States NPIPM (North Plains IPM) app. This app provides not only a pest id tool with morphological drop down, I will discuss this in the ID Tools cat, but also management recommendation for the identified insect.
Record Keeping,

The majority of the apps in this category are “Pay to Play”, which makes since as they deal with data management and storage. Many would also fit the Scouting/Mapping category. As I do not pay for many apps I do not have experience with any of these. However this is the category that I would recommend any group to look at as they should be the all-inclusive app. However, PeRK by the University of Nebraska is a free app designed for field records of pesticide applicators.
ID Tools,


I have added a few apps to this category but my favorites have not changed. I regularly use Plant Images, ID Weeds, and the Pestbook as references. I will add more discuss to app ID tools. The importance of being able to ID weeds and Pest via morphological drop down menus (ID Weeds and NPIPM) is extremely important. Many of the ID tools just have pictures and names. Well is I am using an ID Tool I likely do not know what I am looking at or what it is called.
Crop Tools,
Crop Tools includes my second “Paid in Full” app. And this one hurt a bit more. Not because it cost money but because I have multiple versions of the hard copy. However Field Guide by Purdue is one of my most recommended apps. Field Guide is the electronic version of the Purdue Corn and Soybean Field Guide, which the majority of consultants in the Corn Belt likely have this sitting in their truck. The Stoller apps also have nice very nice image bank of plant developmental phases. FieldGuide and CornAdvisor, another good app, are great examples of what I expect to be coming out of the majority of the Land Grant Universities very soon. Cooperative Extension has hundreds if not thousands of quality hard copy publications just waiting to be turned in to handy dandy apps. To be honest I am working on turning my Nutrient Management Field Guide into an app right now.
Calculators,
Only two apps has been added to this category. I am still using Fert.Removal, HarvestLoss and Growing Degrees on a regular basis.
Sprayer/Chemicals,
Many apps have been added to this group but none of them have been good enough to kick TankMixCalc and SpraySelect of my favorites list.
Fertilizer,
Similar to the Sprayer/Chemicals category several apps have been added to this group, including several from Ok State. For me the Fert Cost Calc is still very useful. I do not get to use the Manure Calc I am very impressed by its layout and user friendliness. This app allows for applicator calibration, nutrient recs and manure value estimator.
Seed Select,
It is no surprise the apps in this category are company created. I will say for the central Great Plains Pioneer’s Canola Calc is very useful tool for selecting canola planting rate providing input for row spacing live plants, seed weight, Germ percent, and survival percent.
To wrap up this blog I want to share with you may new Favorite none ag app. Bump is a huge time saver for anyone who takes pics with your iPhone or iPad. Bump allows easy transfer between mobile devices but more importantly between your mobile device and desktop by a simple tap of the space bar. This file share will go both directions. This means no more emailing pictures from your phone so that you can have them on your desktop. Bump is a iPhone app that can work on the iPad.
When searching with an IPad, remember to switch the search to include IPhone apps, there are some good ones out there that are IPhone only. Check out www.npk.osktate.edu/presentations to see screen shots from many of my favorite apps.