Brian Arnall, Precision Nutrient Management Specialist
Samson Abiola, PNM Ph.D. Student.
Nitrogen is the most yield limiting nutrient in wheat production, but it’s also the most unpredictable. Apply it too early, and you risk losing it to leaching or volatilization before your crop can use it. Apply it too late, and your wheat has already determined its yield potential; you’re just feeding protein at that point. For decades, the conventional wisdom has been to split nitrogen applications: put some down early to get the crop going, then come back later to apply again. But does splitting actually work? And more importantly, when is the optimal window to apply nitrogen if you want to maximize both yield and protein quality? We spent three years across different Oklahoma locations testing every timing scenario to answer these questions.
How We Tested Every Nitrogen Timing Scenario in Oklahoma Wheat
Between 2018 to 2021, we conducted field trials at three Oklahoma locations, including Perkins, Lake Carl Blackwell, and Chickasha, representing different soil types and growing conditions across the state. We tested three nitrogen rates: 0, 90, and 180 lbs N/ac, applied as urea at five critical growth stages based on growing degree days (GDD). These timings were 0 GDD (preplant, before green-up), 30 GDD (early tillering), 60 GDD (active tillering), 90 GDD (late tillering, approximately Feekes 5-6), and 120 GDD (stem elongation, approaching jointing). We also compared single applications at each timing against split applications, where half the nitrogen (45 lbs N ac-1) went down preplant, and the other half was applied in-season (45 lbs N ac-1).
The Sweet Spot: Yield and Protein at the 90 lbs N/ac Rate
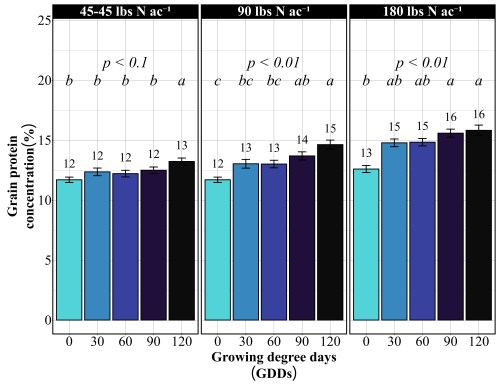
Across all site-years, at the 90 lbs N/ac rate, timing had a significant impact on both yield and protein. The highest yields came from the 30 and 90 GDD timings, producing 62 to 66 bu/ac, with 60 GDD reaching the peak (Figure 1). Protein at these early timings stayed relatively modest at 13%. The 90 GDD timing delivered 62 bu/ac with 14% protein matching the yield of the 30 GDD application but pushing protein a percentage higher (Figure 2). The real problem appeared at 120 GDD. Delaying application until stem elongation dropped yields to just 49 bu/ac, even though protein climbed to 15%. That’s a 13 bushel penalty compared to the 90 GDD timing. At current wheat prices per bushel, that late application may cost farmers over $100 per acre in lost revenue. By 120 GDD, the crop has already determined its yield potential tillers are set, head numbers are locked in and nitrogen applied at this stage can only be directed toward protein synthesis, not building more yield components.
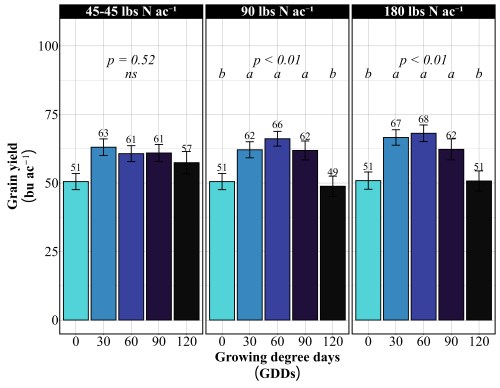
More Nitrogen Does not lead to high yield
Doubling the nitrogen rate to 180 lbs N/ac revealed something critical, more nitrogen doesn’t mean more yield. The yield pattern remained nearly identical to the 90 lbs N/ac rate. The 60 GDD timing produced the highest yield at 68 bu/ac, followed closely by 30 GDD at 67 bu/ac. The 90 GDD timing yielded 62 bu/ac, and the 120 GDD timing again crashed to 51 bu/ac. The only difference between the two rates was protein concentration (Figure 2). At 180 lbs N/ac, protein levels increased across all timings: 13% at preplant, 15% at both 30 and 60 GDD, 15-16% at 90 GDD, and 16% at 120 GDD. This confirms a fundamental principle: once farmers supply enough nitrogen to maximize yield potential, which occurred at 90 lbs N/ac in these trials, additional nitrogen only increases grain protein. It does not build more bushels. Unless farmers are receiving premium payments for high-protein wheat, that extra 90 lbs of nitrogen represents a cost with no yield return.
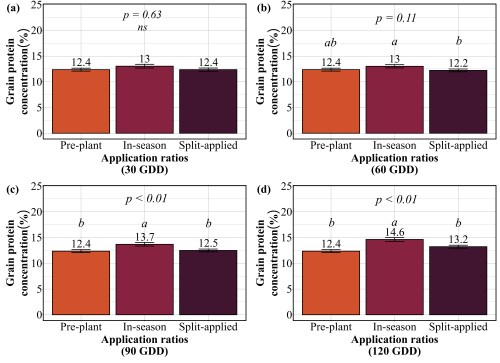
Should farmers split their nitrogen application?
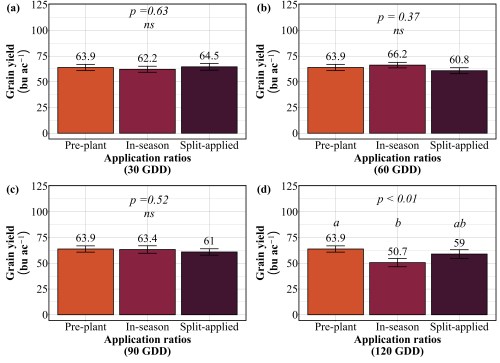
Now that timing has been established as critical, the next question becomes: should farmers split their nitrogen applications, or is a single application sufficient? The conventional recommendation has been to split nitrogen apply part preplant to support early growth and tillering, then return with a second application later in the season to boost protein and finish the crop. But does the data support this practice? We compared three strategies at each timing: applying all nitrogen preplant, applying all nitrogen in-season at the target timing, or splitting nitrogen equally between preplant and in-season timing. The goal was to determine whether the extra trip across the field will deliver better results.
Our findings revealed that splitting provided no consistent advantage. At 30 GDD, all three strategies preplant, in-season, and split performed identically, producing 62-65 bu/ac with 12-13% protein (Figure 3 and 4). No statistical differences existed among them. At 60 GDD, similar pattern was held. Yields ranged from 61 to 66 bu/ac and protein stayed at 12-13% regardless of whether farmers applied all nitrogen preplant, all at 60 GDD, or split between the two. At 90 GDD, the single in-season application actually outperformed the split. While yields remained similar across all three methods (61-64 bu/ac), the in-season application delivered significantly higher protein at 13.7% compared to 12.4% for preplant and 12.5% for split applications. This suggests that concentrating nitrogen at 90 GDD, rather than diluting it across two applications, allows more efficient incorporation into grain protein. The only timing where splits appeared beneficial was 120 GDD, where the split application yielded 59 bu/ac compared to 51 bu/ac for the single late application. But this is not a win for splitting, it simply demonstrates that applying all nitrogen at 120 GDD is too late and putting half down earlier salvages some of the yield loss. Across all timings tested, splitting nitrogen into two applications offered no agronomic advantage over a single well-timed application, meaning farmers are making an extra pass for no gain in yield or protein.
Practical Recommendations for Nitrogen Management
Based on three years of field data, farmers should target the 90 GDD timing (late tillering, Feekes 5-6) for their main nitrogen application to achieve the best balance between yield and protein. This window typically falls in late February to early March in Oklahoma, though farmers should monitor crop development rather than relying solely on the calendar apply when wheat shows multiple tillers, good green color, and vigorous growth. A rate of 90 lbs N/ac maximized yield in these trials; higher rates only increased protein without adding bushels, so farmers should only exceed this rate if receiving premium payments for high-protein wheat. Splitting nitrogen applications provided no advantage at any timing, meaning a single well-timed application at 90 GDD is sufficient for most Oklahoma wheat production systems. The exception would be sandy soils with high leaching potential, where splitting may reduce nitrogen loss. Farmers should avoid delaying applications until 120 GDD or later, as this timing consistently resulted in 15-25 bushel per acre yield losses even though protein increased. For farmers specifically targeting premium protein markets, a two-step strategy works best: apply 90 lbs N/ac at 90 GDD to establish yield potential and baseline protein, then follow with a foliar application of 20-30 lbs N/ac at flowering to push protein above 14% without sacrificing yield. Finally, weather conditions matter hot, dry forecasts increase volatilization risk and reduce uptake efficiency, so farmers should consider moving applications earlier if low humidity conditions are expected.
Split Application Caveat * Note from Arnall.
The caveat to the it only takes one pass, is high yielding >85+ bpa, environments. In these situation I still have not found any value for preplant nitrogen application. I have seen however a split spring application is valuable. Basically putting on 30-50 lbs at green-up, with the rest following at jointing (hollowstem). The method tends to reduce lodging in the high yielding environments.
This work was published in Front Plant Sci. 2025 Nov 6;16:1698494. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1698494
Split nitrogen applications provide no benefit over a single well timed application in rainfed winter wheat
Another reason to N-Rich Strip.
Yet just one more data set showing the value of in-season nitrogen and why the N-Rich Strip concept works so well.
Questions or comments please feel free to reach out.
Brian Arnall b.arnall@okstate.edu
Acknowledgements:
Oklahoma Wheat Commission and Oklahoma Fertilizer Checkoff for Funding.